
Fertigation, a combination of fertilization and irrigation, has gained considerable traction in modern agriculture as a method to efficiently deliver nutrients to plants through fertigation systems. This innovative technique offers a range of benefits, but it also comes with its share of drawbacks. In this comprehensive analysis, we’ll delve into the pros and cons of fertigation to provide a nuanced understanding of its implications for agricultural practices.
Pros and Cons of Fertigation Systems
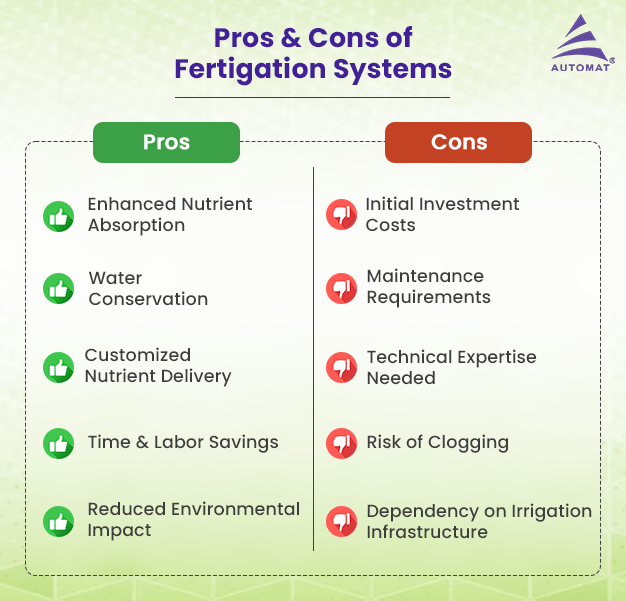
Pros of Fertigation Systems
-
- Enhanced Nutrient Absorption: Fertigation allows for precise and controlled application of nutrients directly to the root zone, ensuring optimal absorption by plants. This targeted approach minimizes nutrient loss and maximizes utilization, leading to improved crop health and yield.
-
- Water Conservation: By incorporating fertilizers into irrigation water, fertigation reduces the need for separate application methods, thereby conserving water resources. This efficiency is particularly advantageous in regions facing water scarcity or undergoing drought conditions.
-
- Customized Nutrient Delivery: Fertigation systems can be tailored to meet the specific nutritional requirements of different crops at various growth stages. This flexibility enables farmers to adjust nutrient formulations according to soil conditions, crop varieties, and environmental factors, optimizing plant growth and productivity.
-
- Time and Labor Savings: Compared to traditional fertilization methods such as broadcasting or foliar spraying, fertigation offers time and labor savings. Automated systems can be programmed to deliver nutrients at precise intervals, reducing manual labor and operational costs for farmers.
-
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Fertigation promotes environmentally responsible farming practices by minimizing nutrient runoff and leaching. By delivering nutrients directly to the root zone, it mitigates the risk of soil and water contamination, contributing to sustainable agricultural practices, alongside water recycling systems that can further reduce environmental impact.
Read more: Fertigation: Pros, Cons, and Impact on Modern Agriculture
Cons of Fertigation Systems
-
- Initial Investment Costs: Implementing a fertigation system requires upfront investment in infrastructure, including specialized equipment such as injectors, pumps, and controllers. While these initial costs can be significant, they are often offset by long-term savings in labor and fertilizer expenses.
-
- Maintenance Requirements: Fertigation systems require regular maintenance and calibration to ensure proper functioning and accurate nutrient delivery. Malfunctions or mismanagement can lead to uneven distribution of fertilizers, compromising crop health and yield potential.
-
- Technical Expertise Needed: Operating a fertigation system effectively requires a certain level of technical knowledge and skill. Farmers must understand the principles of nutrient management, irrigation scheduling, and system maintenance to optimize performance and avoid potential pitfalls.
-
- Risk of Clogging: Fertigation equipment, such as injectors and emitters, may be prone to clogging if not properly maintained or if sediment-laden water is used. Clogs can disrupt nutrient flow and result in uneven distribution, necessitating frequent monitoring and cleaning to prevent downtime and crop damage.
-
- Dependency on Irrigation Infrastructure: Fertigation relies on existing irrigation infrastructure, such as drip or sprinkler systems, for nutrient delivery. In regions with inadequate or unreliable irrigation infrastructure, implementing fertigation may pose logistical challenges and limit its effectiveness.
Also read: Increase Crop Yield with Power of Smart Fertigation Technology
Conclusion
According to a report, when water and fertilizer are supplied evenly to all the crops through fertigation there is possibility for getting 25-50 per cent higher yield. Fertigation offers a host of advantages, including enhanced nutrient absorption, water conservation, and customized nutrient delivery, making it a valuable tool for modern agriculture. However, it’s essential to weigh these benefits against potential drawbacks such as initial investment costs, maintenance requirements, and technical expertise needed. By carefully evaluating the pros and cons, farmers can make informed decisions about incorporating fertigation into their agricultural practices, maximizing productivity while minimizing environmental impact.
Additionally, Automat Industries Pvt. Ltd. offers a variety of fertigation equipment and solutions to cater to the diverse needs of farmers, making it easier to adopt and implement this sustainable and efficient agricultural practice.




